RayMaster is a simulation program that calculates light beam divergence using ray optics in 2 dimensional space. Optical components such as Ball lens, transparent plate, opaque plate, mirror can be placed. Ray traces will be displayed according to the ray optics when a beam is launched after a beam source is placed.
Features
- Easy to learn how to use. Place optical components and a beam source. Then, launch the beam. That's all.
- Plates, mirror, absorber, filters, ball lens and fiber are supported
- More complex optical component can be implemented by placing the above simple components
- Several beam shapes such as collimated beam, diverged beam, large cord waveguide can be chosen
- Beam launching angle and divergence angle can be adjusted
The following table shows the optical components that Ray Master supports.
| Category | Optical components | Description |
| Plate | Transparent plate | Only transmissions are shown |
| Opaque plate | Only reflections are shown | |
| Surface | Transmissions and reflections are shown | |
| Mirror | Mirror | Only reflections are shown, Reflectance=100% |
| Absorber | Absorber | Absorb the light |
| Filter | Transparent filter | Only transmissions are shown Transmittance can be specified |
| Opaque filter | Only reflections are shown Reflectance can be specified |
|
| Ball lens | Ball lens | Semi sphere type ball lens. Transmissions or reflections can be shown |
| Fiber | Fiber | It measures the amount of coupled light |
If a beam is launced into a component, transmitted and reflected beams are displayed.
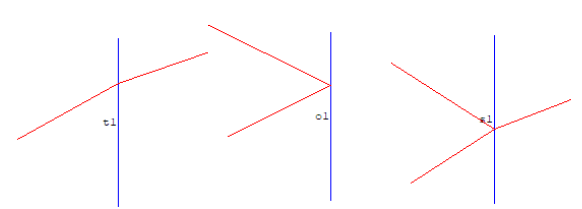
Red lines denote beam. First plate is a transparent plate so that the transmission is shown. Second plate is an opaque plate and the reflection is shown. The last plate is a surface that shows transmission and reflection.
There are 3 types of launching beams. Collimated beam, diverged beam and large core waveguide.
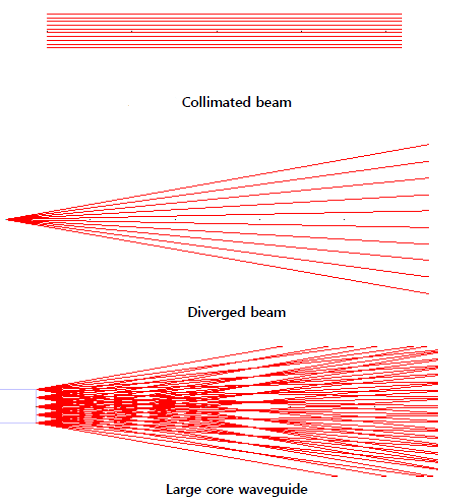
The number of rays and beam divergence can be selected. The ray traces will be displayed after entering the launch parameters. The following example shows that diverged beams are launched to a ball lens.
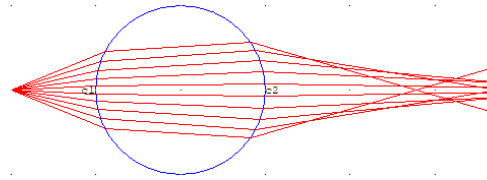
If a diverged beam is incident into a prism, the result will be as follows.
Screen shots