Features
- Constant current mode is supported
- High current (Up to 20A, actual maximum current can vary according to the LED voltage), High voltage(Up to 40V, actual maximum voltage can vary according to the LED current)
- Low heat generation implemented using headroom voltage control
- Automatic shutdown for safety is provided (High voltage, High current, High temperature shutdown)
- Computer can control LED current setting and LED On/Off via USB interface. Control GUI is provided.
- Actual LED current, LED voltage, LED temperature and driver temperature are monitored
- RS232 serial port is supported for remote control
- All LED drivers are fully customizable. No of channel, max LED current, LED voltage range, and more can be selected.
Constant current mode vs Constant voltage mode
A LED can operate in either constant current mode or constant voltage mode. Constant voltage mode is simpler way to drive a LED, but it can cause unstable operation. A LED is a kind of a diode. While the LED voltage is almost constant, the LED current can vary over a wider range. Small changes of the LED voltage can lead to large changes in the LED current. In general, allowed operating LED current is limited and the LED can be damaged if the LED current exceeds the allowed LED current. Moreover, the LED voltage and current will vary while the LED is running. The LED current will increase if constant voltage is applied to the LED continuously. In addition, constant current mode is a better way to maintain the LED brightness because the intensity of LED is proportional to the LED current.
LED driver block diagram
Our LED driver supplies constant current to LEDs. The LED voltage will vary automatically according to the LED current. The following picture is the block diagram of the LED driver.
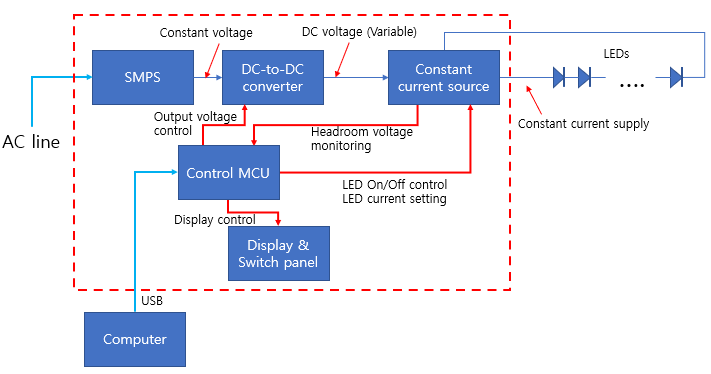
The LED driver has a MCU that controls the constant current source and DC-to-DC converter. The MCU monitors the LED driver status such as the temperature of the LED and current source, the LED current, the LED voltage, and etc. The constant current source supplies the constant current to LEDs. The driving current setting of the current source can be changed by the MCU. The current source can be turned on or off by the MCU as well. The LED driver can provide wide range of LED operation voltage because the MCU controls the DC-to-DC converter and constant current source. Any LED array configuration can be connected to the LED driver. In this case, the LED driver can not know the LED operating voltage. The applied voltage to the LED array should be large enough to turn on the LEDs, but If the applied voltage is too large, the current source generates large amount of heat. The excessive voltage can cause burnout of the current source. The MCU monitors the LED voltage and controls the output voltage of the DC-to-DC converter to minimize the headroom voltage. This mechanism reduces the heat generation of the current source and ensure the stable operation of the LED driver.
Safety features
The LED driver has several safety features. The MCU inside the LED driver monitors the LED temperature and the current source temperature. The current source will be turned off automatically if the temperature exceeds the safety temperature. If the headroom voltage is too large or the difference between the setting current and actual current is too big, the MCU will turn off the current source.
Exterior example of the LED driver
The following picture shows the exterior of the LED driver.


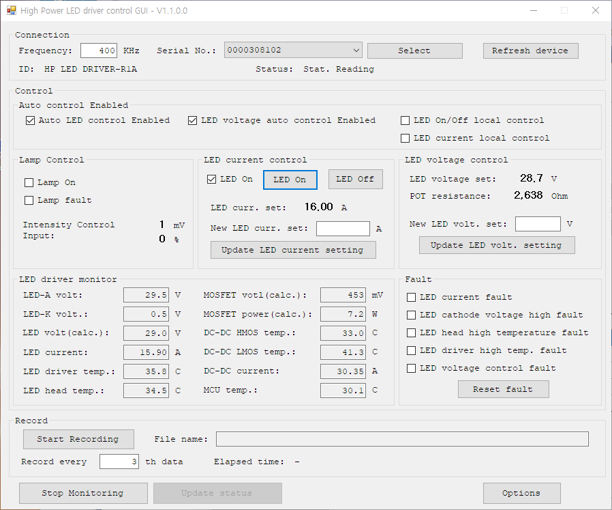
The Control GUI
The following picture shows the screen capture of the control GUI. The contron GUI configuration can vary depending on the LED driver.